
Explain the nucleus of a cell with a neat labeled diagram Science
Course: High school biology > Unit 2. Lesson 2: Basic cell structures. Introduction to the cell. Introduction to cilia, flagella and pseudopodia. Basic cell structures review. Identifying cell structures. Basic cell structures. Science >. High school biology >.
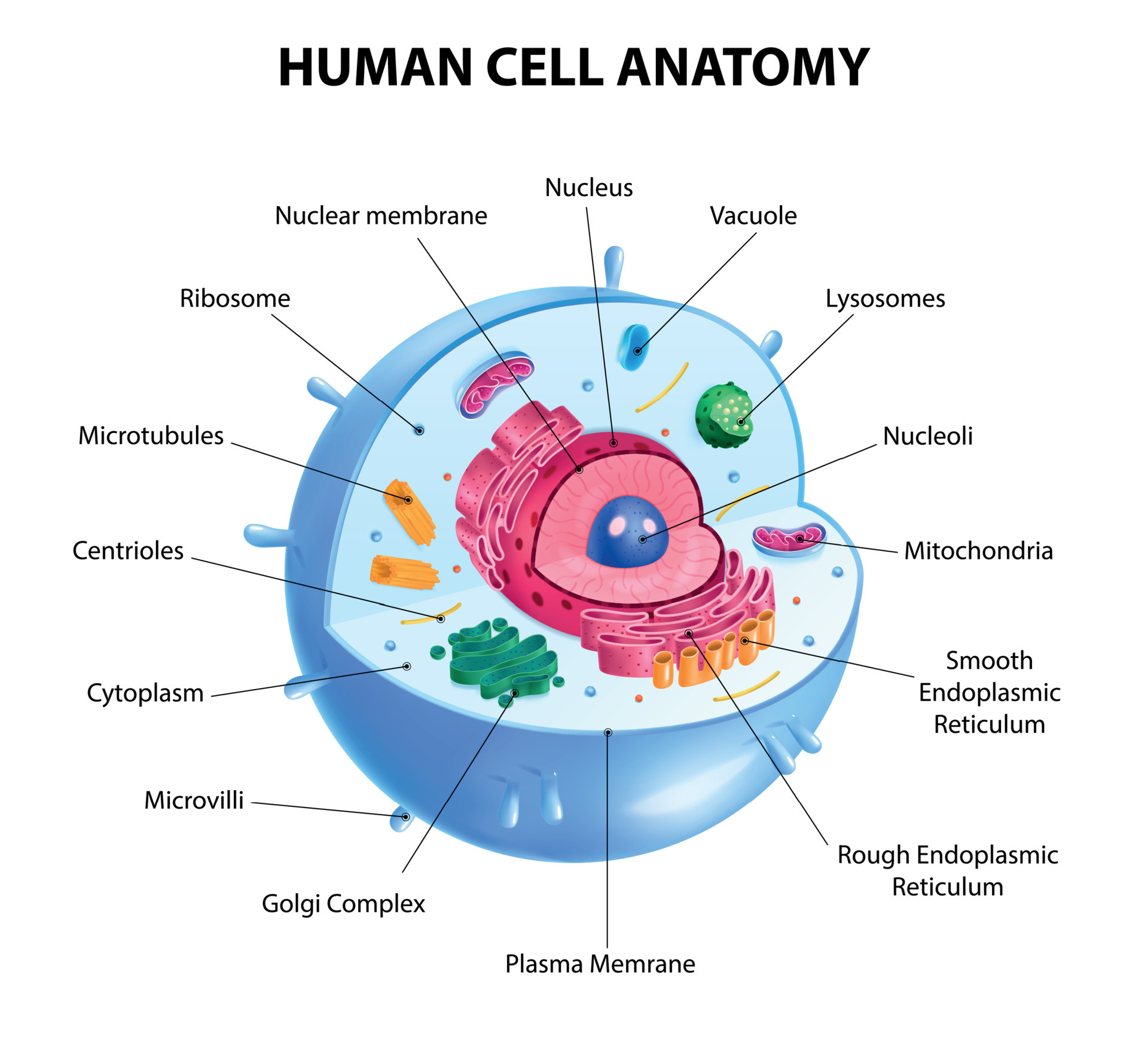
Human Cell Diagram 6406474 Vector Art at Vecteezy
In other words, a diagram of the membrane (like the one below) is just a snapshot of a dynamic process in which phospholipids and proteins are continually sliding past one another.

Pin by james paterson on A (growing) list of people, places and things
cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. These cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become.
Cell Membrane Images Worksheet Answers
Eukaryotic cells,one of the two major types of cells, have a nucleus. A nucleus is a large structure that controls the workings of the cell because it contains the genes. Both ani-mals and plants have eukaryotic cells. Outer Boundaries of Animal and Plant Cells Animal and plant cells are surrounded by a Chapter 3 cell structure and function cells

Cell Structure
Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA and ribosomes, not all cells are the same. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.

NCERT Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
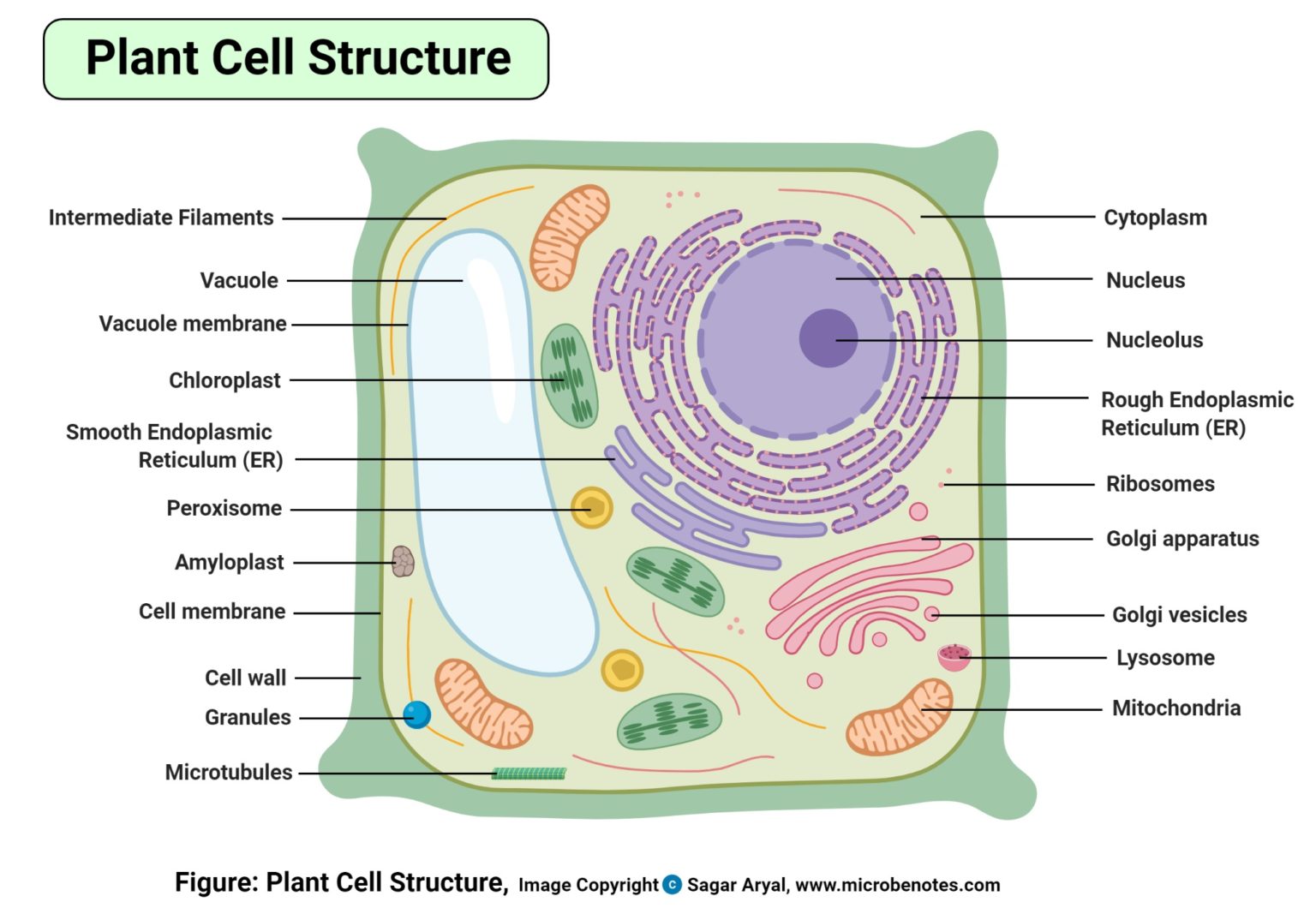
1. Plasma membrane: a selective barrier which encloses a cell (plant and bacteria cells also contain a cell wall ). 2. Cytosol: located inside the plasma membrane, this is a jelly-like fluid that supports organelles and other cellular components. 3. Cytoplasm: the cytosol and all the organelles other than the nucleus. 4.
Structure of cell Cell structure and functions, Class 8
A brief explanation of the different parts of an animal cell along with a well-labelled diagram is mentioned below for reference. Also Read Different between Plant Cell and Animal Cell Well-Labelled Diagram of Animal Cell The Cell Organelles are membrane-bound, present within the cells.

View 20 All Parts Of An Animal Cell Labeled Eporali Wallpaper
Cell Membrane: The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a selectively permeable lipid bilayer that encloses the contents of the cell and regulates the transport of materials into and out of it. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the jelly-like fluid that gives a cell is shape and contains the molecules the cell needs for its processes.

Luke's Place This blog is about my school year and myself.
A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles. Cell membrane Every cell in the body is enclosed by a cell ( Plasma) membrane.

Label the Parts of the Plant and Animal Cell Biology LibreTexts
Figure 6.4 Animal cell mitosis is divided into five stages—prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase—visualized here by light microscopy with fluorescence. Mitosis is usually accompanied by cytokinesis, shown here by a transmission electron microscope. (credit "diagrams": modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal; credit "mitosis micrographs": modification of work by.
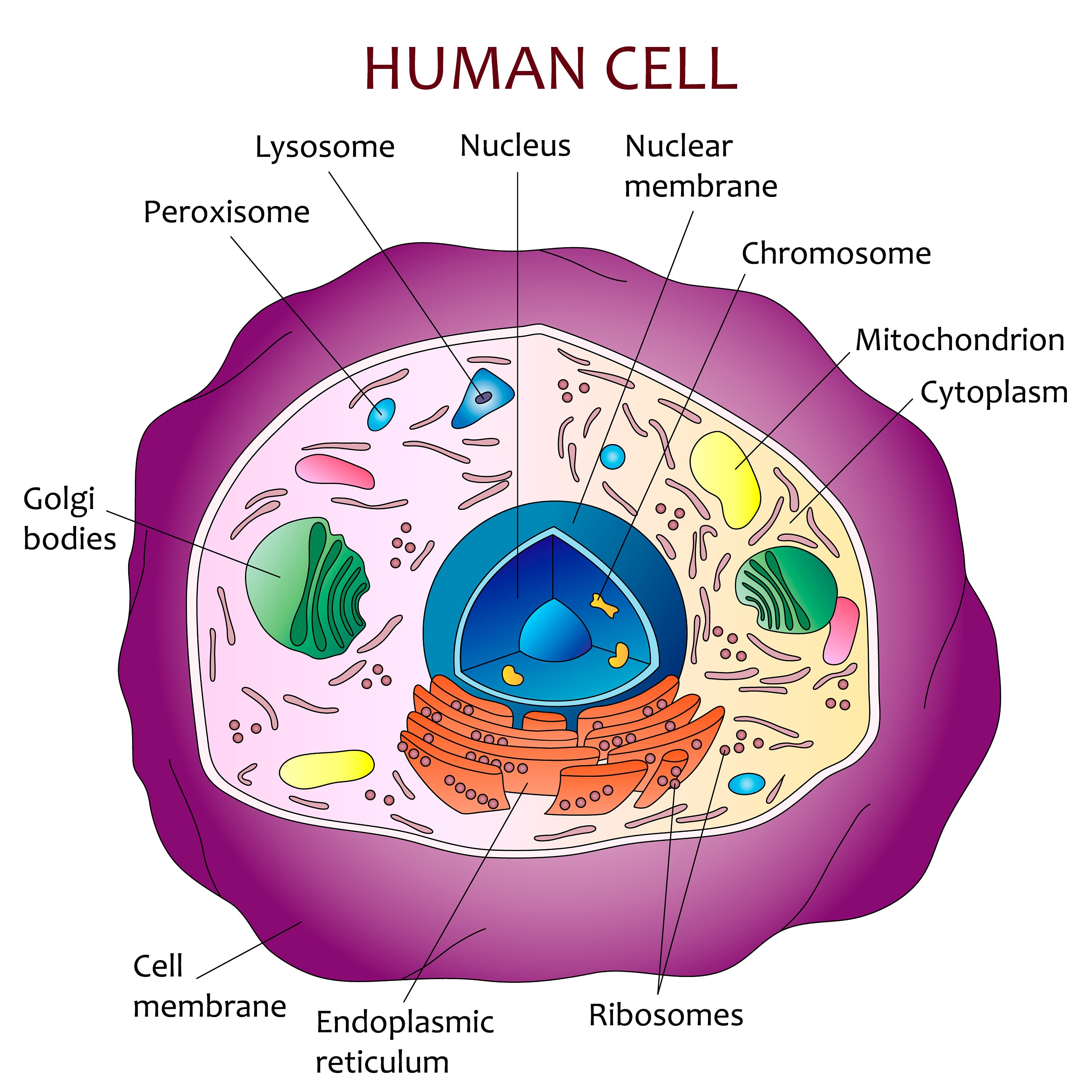
Human cell diagram Etsy
A prokaryote is a simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.

[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Cytosol
The plasma (cell) membrane separates the inner environment of a cell from the extracellular fluid. It is composed of a fluid phospholipid bilayer (two layers of phospholipids) as shown in figure 4.1.2 4.1. 2 below, and other molecules. Not many substances can cross the phospholipid bilayer, so it serves to separate the inside of the cell from.
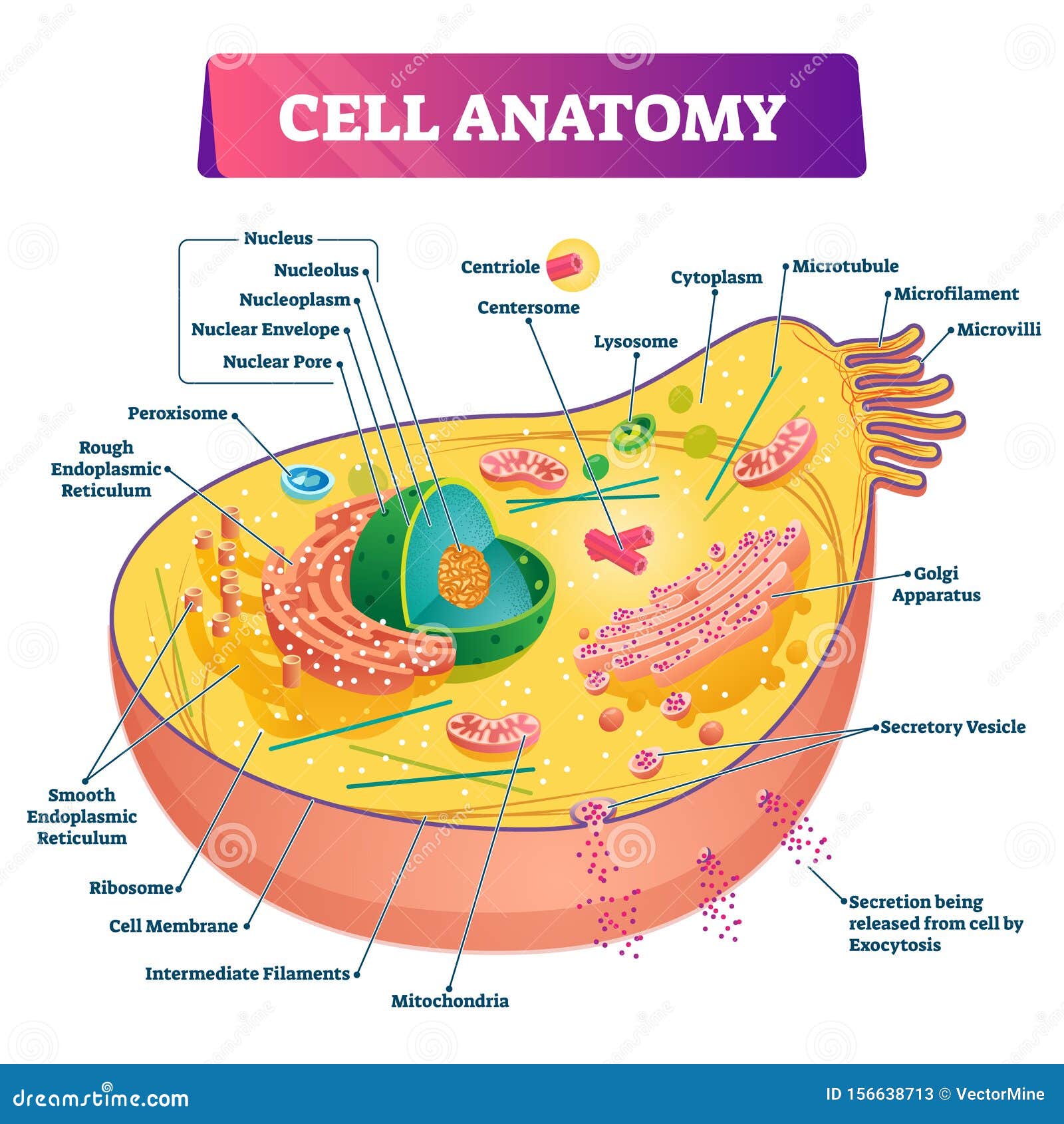
Cell Anatomy Vector Illustration. Labeled Educational Structure Diagram
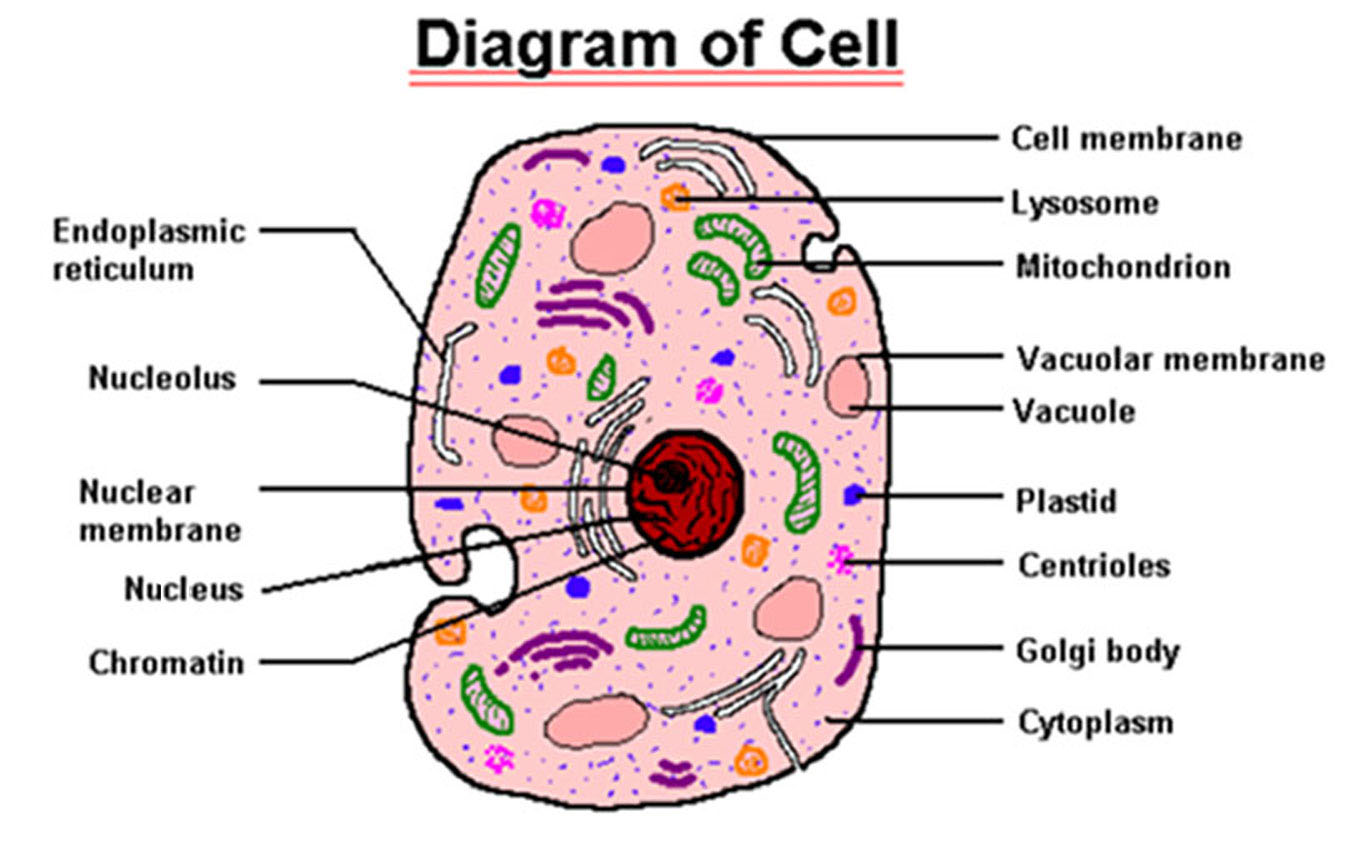
Cell diagram labeled Cell diagram unlabeled Learn faster with interactive cell quizzes Sources + Show all What are the parts of a cell? There exist two general classes of cells: Prokaryotic cells: Simple, self-sustaining cells (bacteria and archaea) Eukaryotic cells: Complex, non self-sustaining cells (found in animals, plants, algae and fungi)
Education 645 High School Biology
Cell Parts ID Game. Test your knowledge by identifying the parts of the cell. Choose cell type (s): Animal Plant Fungus Bacterium. Choose difficulty: Beginner Advanced Expert. Choose to display: Part name Clue. Play.

Animal Cell Diagrams Labeled Printable 101 Diagrams
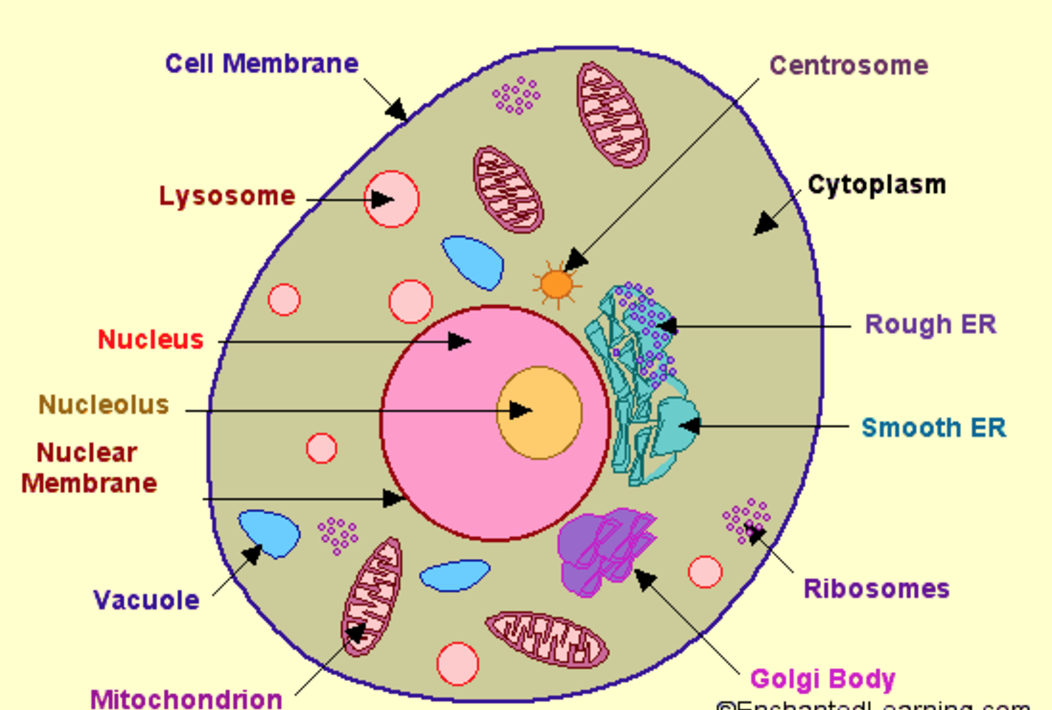
The nucleus is a large organelle that contains the cell's genetic information. Most cells have only one nucleus, but some have more than one, and others—like mature red blood cells—don't have one at all. Within the nucleus is a spherical body known as the nucleolus, which contains clusters of protein, DNA, and RNA.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12788/histology-eukaryotic-cell_english.jpg)
Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes Kenhub
Middle school biology - NGSS > > Cell parts and functions Cell parts and functions Google Classroom Review your understanding of cell parts and functions in this free article aligned to NGSS standards. Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out.