Low Fidelity Wireframes [What are they + Examples] Alvaro Trigo's Blog
As part of an engagement with the company, you can work with them to develop both low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes before manufacturing a large quantity of your product. Their low-fidelity prototypes are typically CAD drawings or sketches, while the high-fidelity prototypes are typically 3D printed models using affordable materials.
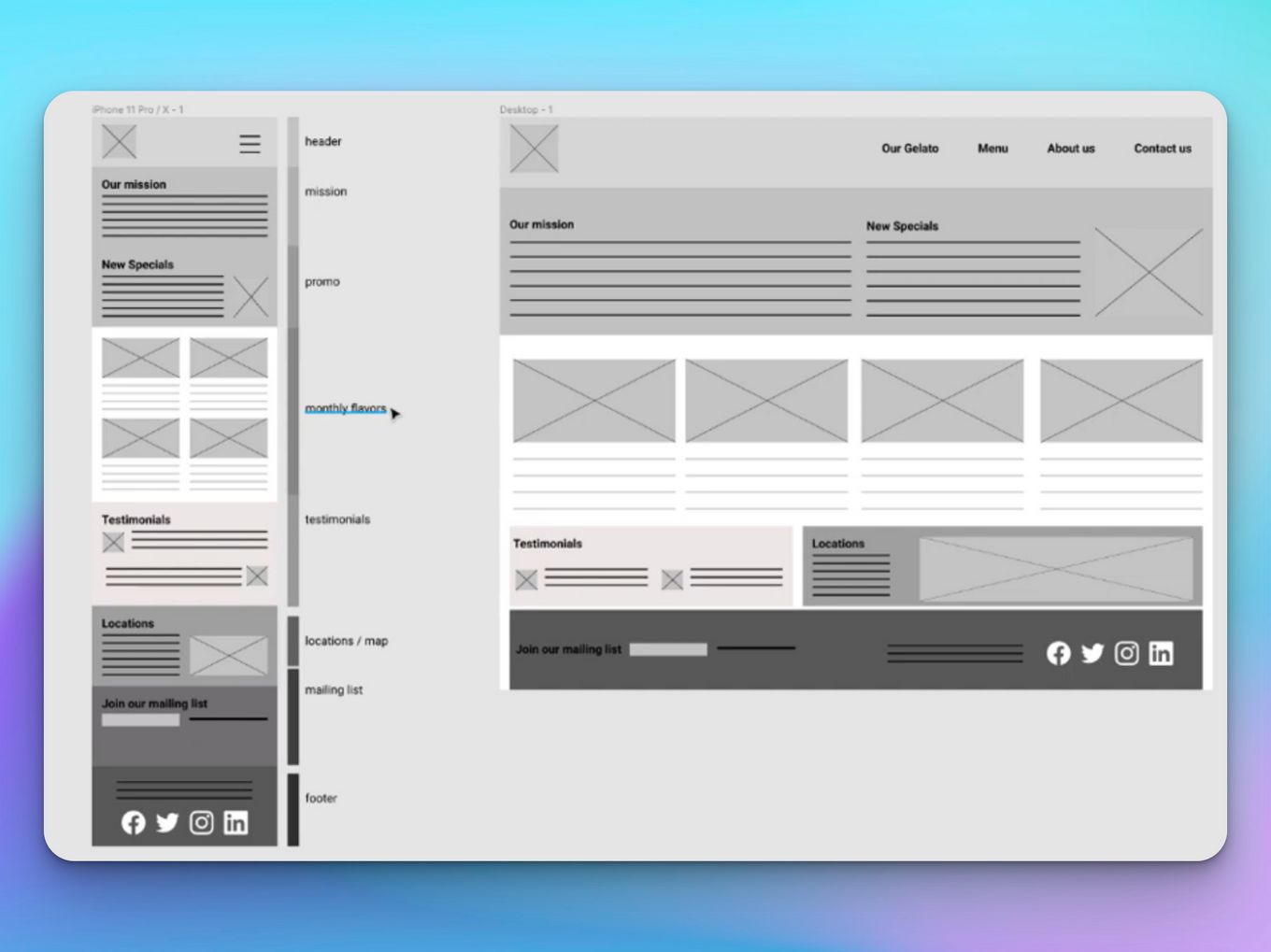
Low Fidelity Wireframes [What are they + Examples] Alvaro Trigo's Blog
Low-fidelity prototypes are an inexpensive and fast way to test a rough outline of your design ideas. Low-fidelity prototypes help you find potential pitfalls within your design earlier, allowing you to eliminate bad design ideas. Testing your prototypes validates your hypotheses and improves your solutions.
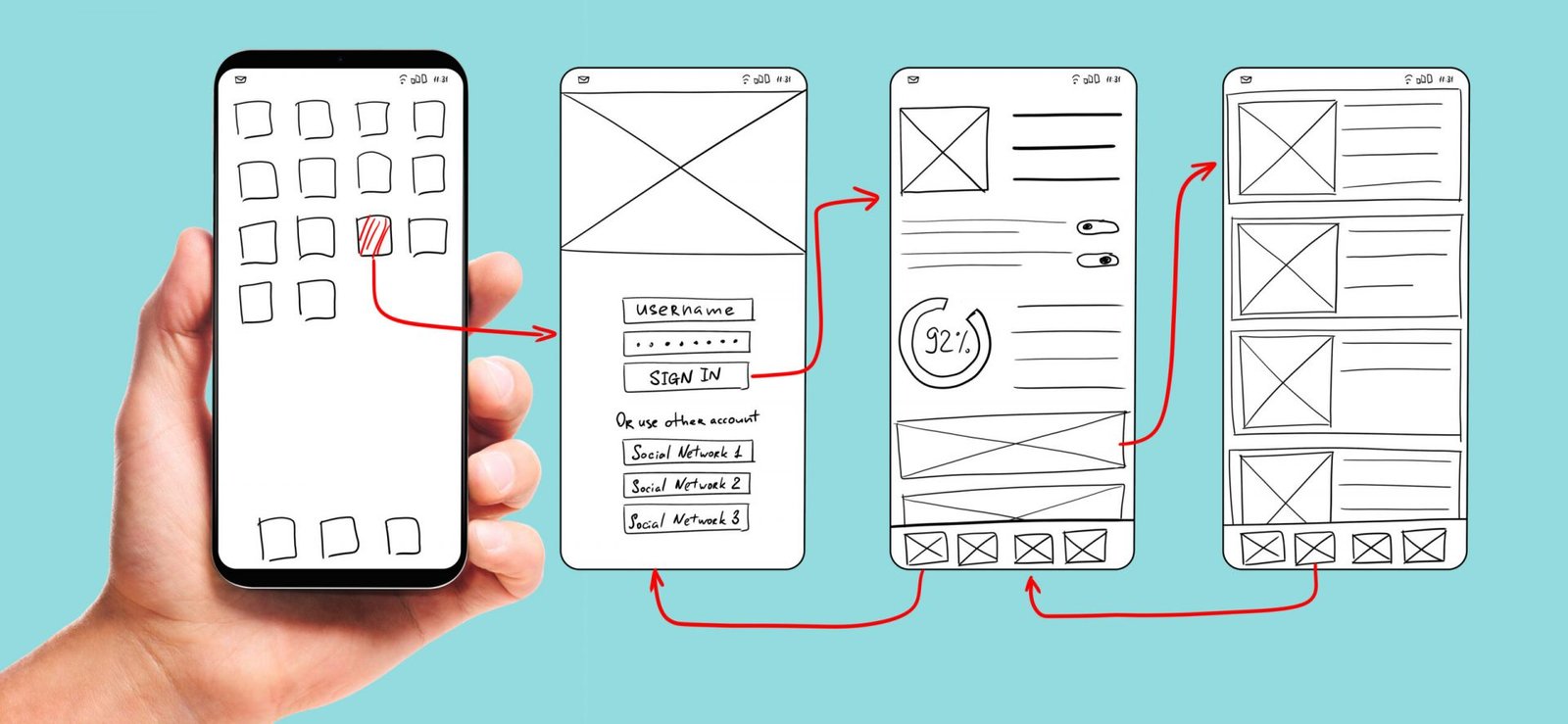
How To Create A LowFidelity Prototype Like An App Expert ThinkLions
Low fidelity design has less detail, but a low fidelity prototype draws its strength from being the quickest and easiest way to explore function, interactivity, and overall structure of a product before dedicating the time and money into a hi-fi prototype or design. Another name for a low fidelity prototype is a wireframe.
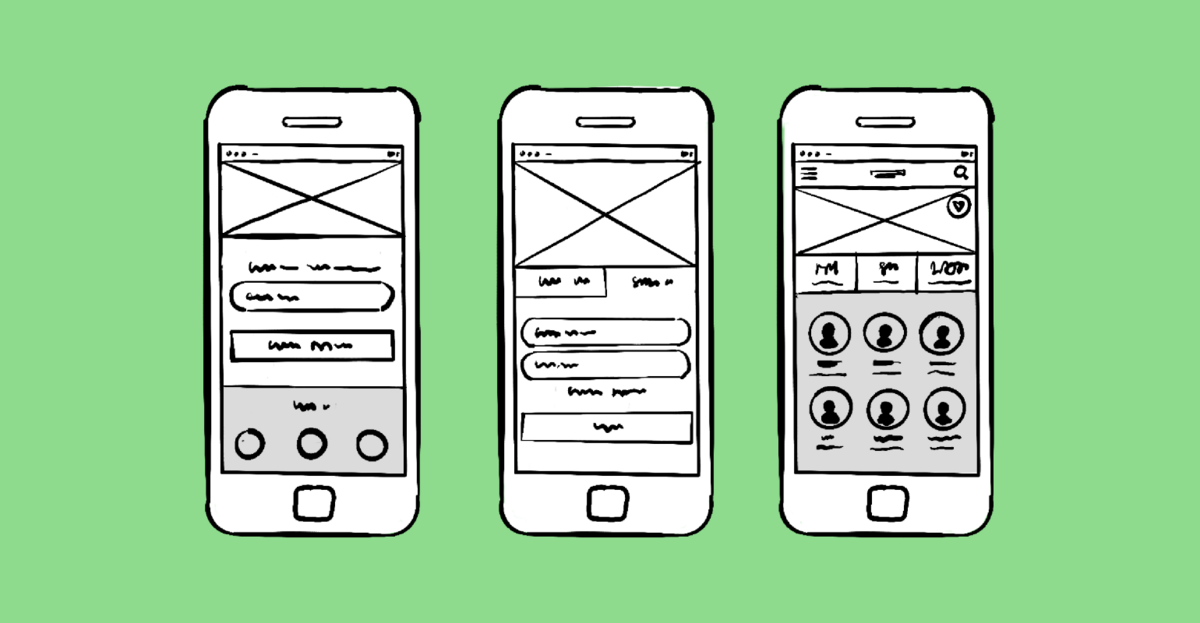
What is an app prototype and why make one?
Low-fidelity prototypes are rough representations of concepts that help us to validate those concepts early on in the design process. Throughout this article, Laura Busche will look at some of the features that make low-fidelity prototyping a unique tool to radically improve your work and to build an environment in which users' needs can be truly realized.

Why is low fidelity wireframe important in product design? by Winnie
Low-fidelity (lo-fi) prototyping is a quick and easy way to translate high-level design concepts into tangible and testable artifacts. The first and most important role of lo-fi prototypes is to check and test functionality rather than the visual appearance of the product. Here are the basic characteristics of low-fidelity prototyping:
Low Fidelity vs High Fidelity by Thilina Pitiwala on Dribbble
Low-fidelity prototypes allow you to better test the user interface (UI) while high-fidelity prototypes allow you to also test for user experience (UX). In most cases, it is best to test multiple prototypes, beginning with the most minimal low-fidelity model and building your way up. 3) Build It. Finally, it's time to build your prototype.
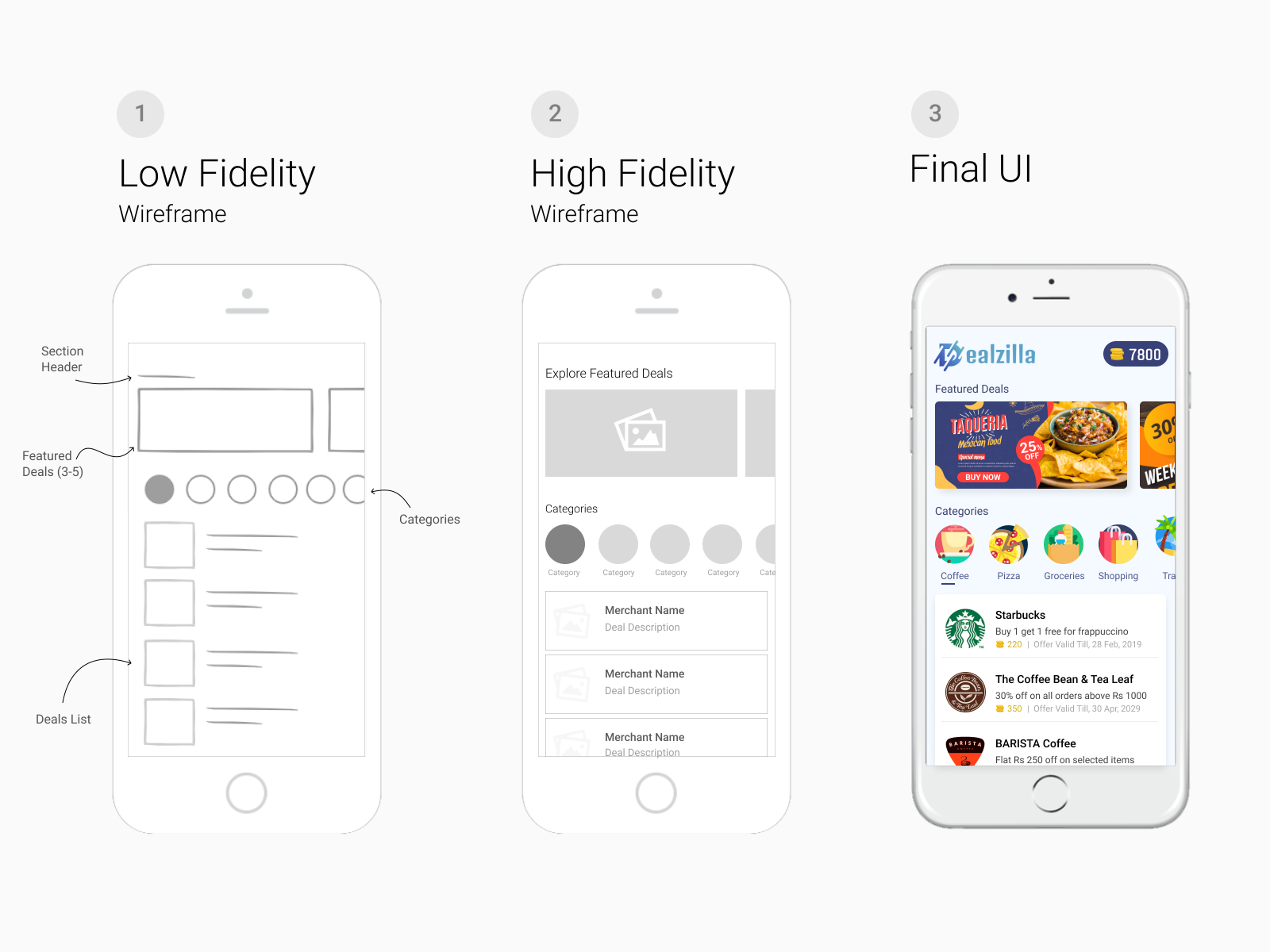
Low Fidelity Wireframes [What are they + Examples] Alvaro Trigo's Blog
By definition, lo-fi stands for "low fidelity.". Fidelity is a synonym for "quality" in the music world, meaning lo-fi technically means low-quality music. Before anyone gets offended by that, it doesn't mean the music is terrible. Lo-fi typically refers to low recording quality, including background noise, audio imperfections, and.
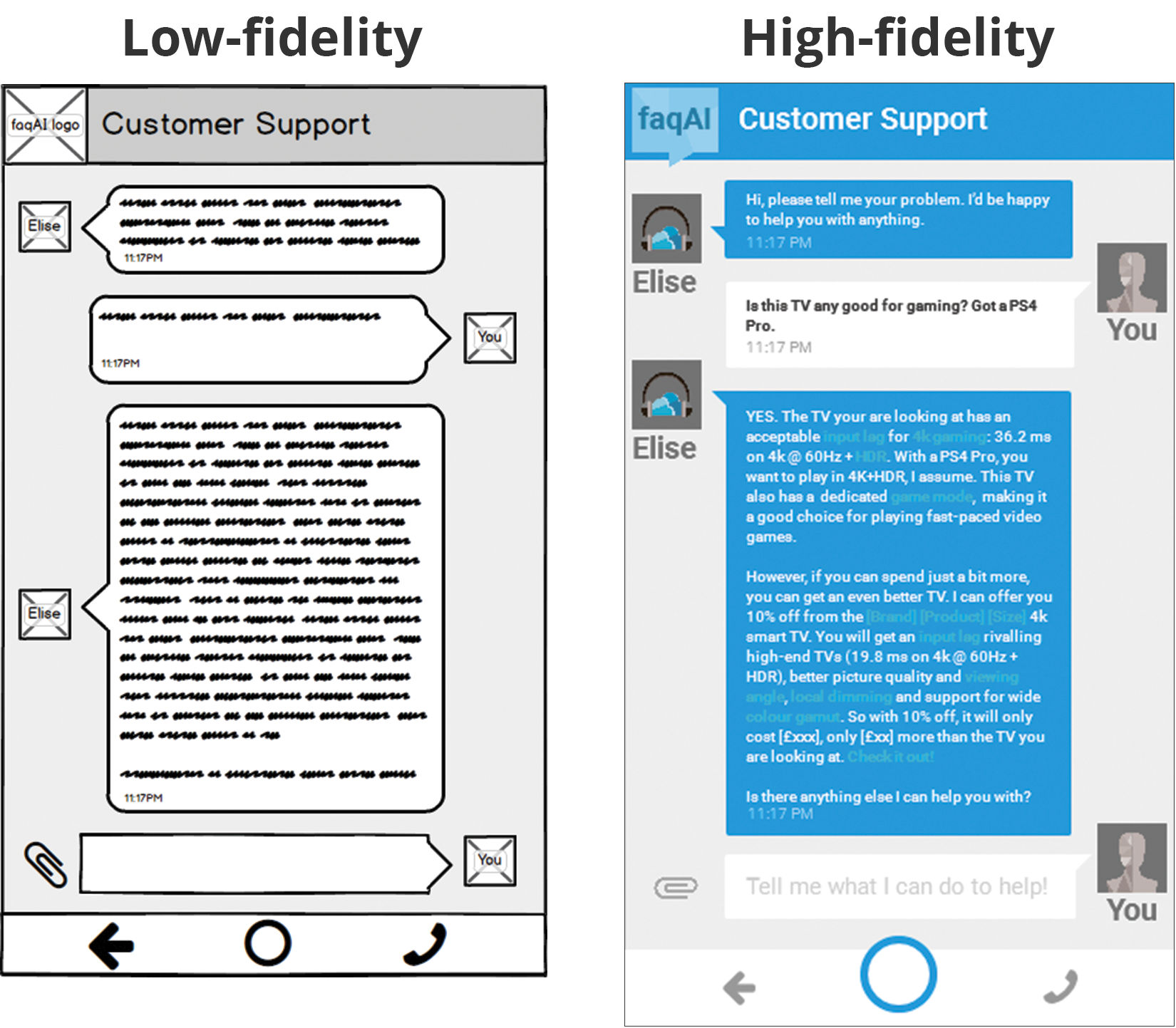
Lowfidelity versus highfidelity wireframes User Experience Mapping
Low fidelity design allows the product team to test design ideas and user flows before committing to a particular approach. Low fidelity design can be created both on paper (i.e., paper sketches, paper prototypes) or digitally (i.e., using prototyping tools like Balsamiq, Sketch, or Invision). When to use low fidelity design

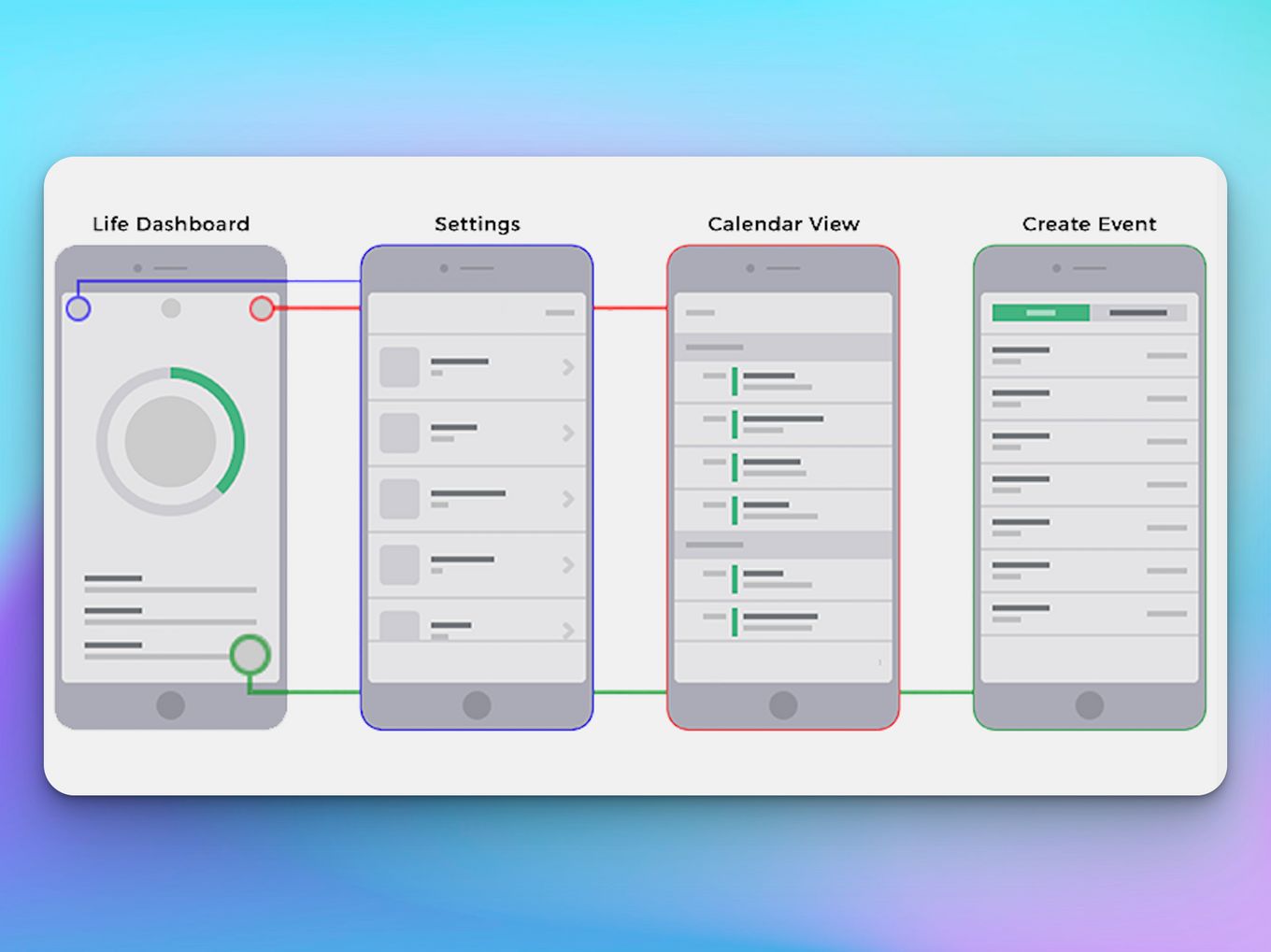
HighFidelity & LowFidelity Prototyping What, How and Why?
Low-fidelity prototyping is a simple diagram of an early-stage design concept. UX designers use it to quickly test and validate their ideas, identify gaps and pitfalls, and discard products that don't resonate with users. Learn how to make low-fidelity prototypes with Figma in four simple steps, and see the benefits of low-fidelity prototyping for user experience.

Low Fidelity Downtown New York 197484 — The Waverly Press
Learn more about Low-Fidelity Prototypes. Take a deep dive into Low-Fidelity Prototypes with our course User Experience: The Beginner's Guide . If you've heard the term user experience design and been overwhelmed by all the jargon, then you're not alone. In fact, most practicing UX designers struggle to explain what they do!

Low Fidelity Wireframe Sequence by Blake Howard on Dribbble
Learn the benefits and drawbacks of low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototyping, and how to choose the right fidelity for your design needs. Low-fidelity prototypes are simple and low-tech, while high-fidelity prototypes are highly functional and interactive.
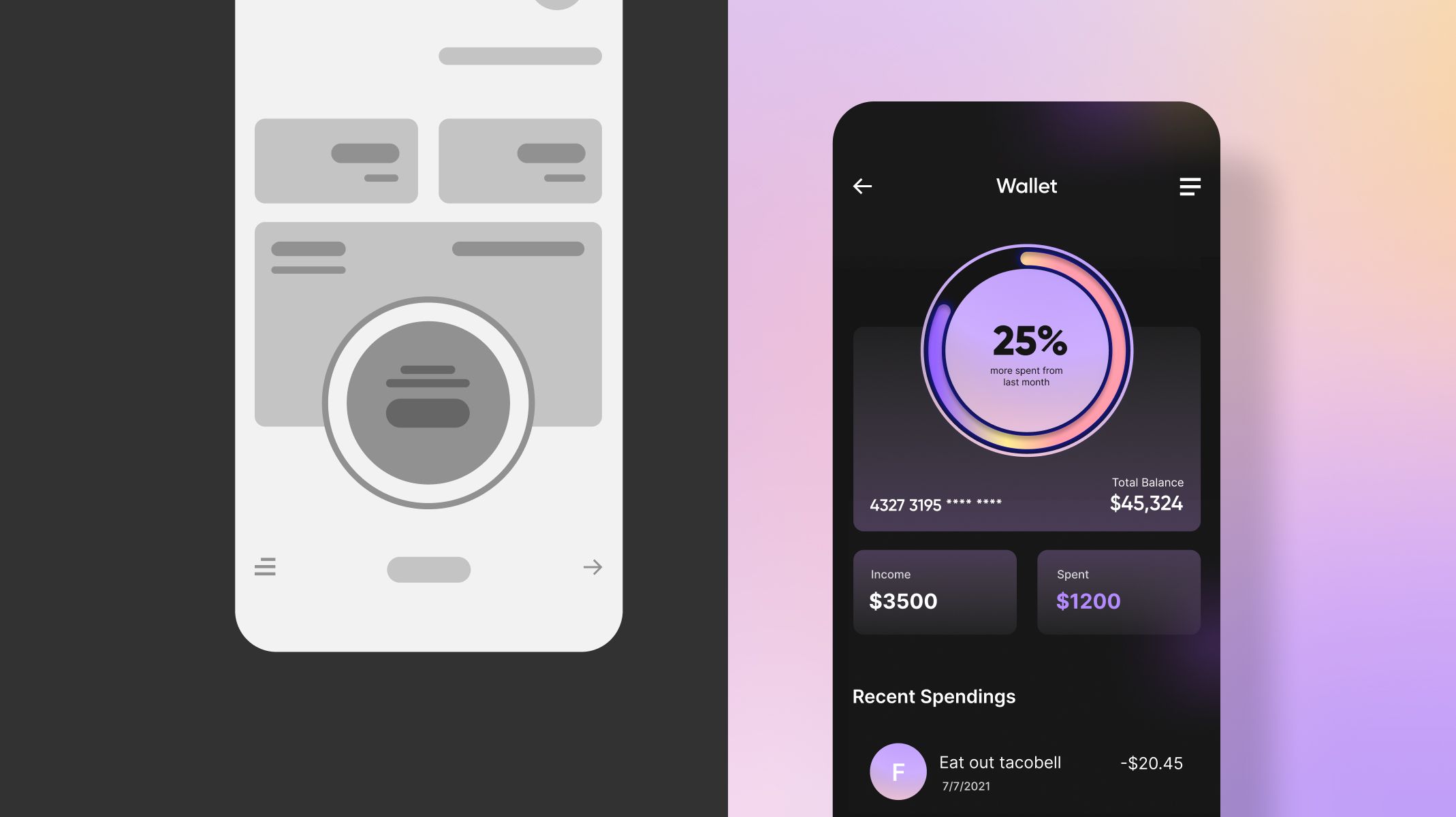
The Differences Between Low Fidelity vs. High Fidelity Prototyping
Low-fidelity prototypes put less pressure on users. If a design seems incomplete, users usually have no idea whether it took a minute or months to create it. They may better understand that you are indeed testing the design and not them, feel less obliged to be successful, and be more likely to express negative reactions..

Low Fidelity vs High Fidelity Wireframe Differences Between Wireframes
What Is Low Fidelity? Low-fidelity prototypes are fast and easy for designers to make, and they represent a concept or product without focusing on the visuals or interactive features. When you design a prototype, it can have either low or high fidelity. Fidelity refers to how much a prototype resembles the actual product which includes the.
Low Fidelity Movie Reviews
A low-fidelity piece might be muffled or obscured by other noises, and sometimes there may even be mistakes by the musician on the record. Punk music is often characteristically lo-fi for example — the low-quality recording gives it that raw DIY sound. However, when people talk about lo-fi nowadays this is rarely what they mean.

Low Fidelity Wireframes [What are they + Examples] Alvaro Trigo's Blog
1. Low Fidelity Motion Prototype Example. This low-fi prototype shows the second menu motions clearly without focusing too much on its UI details. 2. Low Fidelity UX Prototype Example for a Website Builder. This low fidelity UX prototype presents the page layouts, navigation systems and user flows of interactions clearly without too much UI.

Lowfidelity vs. highfidelity prototyping by ⌘⌥ Rafael Barbosa Medium
We should use low-fidelity prototypes to test only for broad concepts rather than fine details such as animations. This is because low-fidelity prototypes tend to lack details and realism. For instance, we can use low-fidelity paper prototypes to test different solutions for a problem at the very early stages of ideation.